一文快速详解ES6~ES12的全部特性!
已收录本篇文章给大家整理分享一下ECMAScript特性,带大家花一个小时,迅速了解ES6~ES12的全部特性。有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对大家有所帮助。 作为一个喜欢动手敲代码的小菜鸟,我认为代码应该亲自敲一遍,才能更好的熟记于心,所以今天就介绍一下有关 ES6 ~ ES12 的特性。如果你对ES有关的使用有盲区,或则不太了解新特性相信这篇文章应该能够很好的帮助你~ 为了更好地理解,我们以 案例 的模式去讲解,这样更好的理解,同时,案列也支持开发者模式下的调试,希望大家可以多多支持~ ECMAScript是一种由Ecma国际(前身为欧洲计算机制造商协会,European Computer Manufacturers Association)通过ECMA-262标准化的脚本程序设计语言。也可以说是JavaScript的一个标准 在程序员的世界只有两个版本: 关于 let、const 和 var 之间的区别: 另外,当 正则其实是一个非常难懂的知识点,要是有人能完全掌握,那真的是非常厉害,在这里就简单的说下 首先分为两种风格: JS分格: RegExp() perl风格: / 规则 /选项,且可以跟多个,不分顺序 这里介绍一个正则表达式在线测试(附有常见的正则表达式):正则在线测试 箭头函数与普通函数的区别 Set 是ES6中新的数据结构,是类似数组,但成员的值是唯一的,没有重复的值 声明: 属性: 方法: 特别注意: 应用: 定义: 和Set的结构,但成员值只能为对象 声明: 方法: 注意: 推荐指数: ⭐️⭐️ Map 是ES6中新的数据结构,是类似对象,成员键是任何类型的值 声明: 属性: 方法: 特别注意: 定义: 和Map的结构,但成员值只能为对象 声明: 方法: Symbol 是ES6中引入的原始数据类型,代表着 声明: 参数: string(可选) 方法: Proxy用于修改某些操作的默认行为,等同于在语言层面做出修改,所以属于一种“元编程”(meta programming),即对编程语言进行编程 可以这样理解,Proxy就是在目标对象之前设置的一层 Proxy 在这里可以理解为 声明: 方法: Reflect 与 Proxy 类似,只是保持 Reflect 的方法与 Proxy 的方法一一对应,这里就不进行介绍了 Class: 对一类具有共同特征的事物的抽象(构造函数语法糖) 定义: 包含异步操作结果的对象 状态: 注意: Generator: 是可以用来控制迭代器的函数,也是封装多个内部状态的异步编程解决方案,也叫生成器函数 参数说明 Iterator是一种接口,为各种不同的数据结构提供统一的访问机制。任何数据结构只要部署Iterator接口,就可以完成遍历操作(即依次处理该数据结构的所有成员)。 Iterator的作用: 注意: 在早期,使用立即执行函数实现模块化是常见的手段,通过函数作用域解决了命名冲突、污染全局作用域的问题 使用模块化的好处: 方案: 作用: 将异步函数改为同步函数,(Generator的语法糖) 特别注意: 这里分为两种情况: 是否为 promise 对象 如果不是promise , await会阻塞后面的代码,先执行async外面的同步代码,同步代码执行完,再回到async内部,把这个非promise的东西,作为 await表达式的结果。 如果它等到的是一个 promise 对象,await 也会暂停async后面的代码,先执行async外面的同步代码,等着 Promise 对象 fulfilled,然后把 resolve 的参数作为 await 表达式的运算结果。 优点: 缺点: Promise.finally() for-await-of: 异步迭代器,循环等待每个 在 ES10 中,try catch 可忽略 catch的参数 特别注意: 在ES6中一共有7种,分别是: 其中 而在ES11后新增一中,为 8中 分别是: Promise.allSettled(): replaceAll() Promise.any() 【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】 以上就是一文快速详解ES6~ES12的全部特性!的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

ES5 和 ES6,说是ES6,实际上是2015年发布的,也是大前端时代正式开始的时间,也就是说以2015年为界限,2015年之前叫 ES5 ,2016年之后则统称ES6ES6特性的可看看阮一峰老师的《ES6标准入门》声明
let & const
const声明了一个对象,对象能的属性可以改变,因为:const声明的obj只保存着其对象的引用地址,只要地址不变,便不会出错解构赋值
数组的解构
...进行解构,代表剩余全部undefined
let [a, b, c] = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(a, b, c) // 1 2 3
let [a, , c] = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(a, , c) // 1 3
let [a, b, ...c] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(a, b, c) // 1 2 [3, 4, 5]
let [a, b, ...c] = [1]
console.log(a, b, c) // 1 undefined []
let [a = 1, b = a] = []
const.log(a, b) // 1 1
let [a = 1, b = a] = [2]
const.log(a, b) // 2 2
对象的结构
undefined
:,他相当于别名 let { a, b } = { a: 1, b: 2 };
console.log(a, b); // 1 2
let { a } = { b: 2 };
console.log(a); // undefined
let { a, b = 2 } = { a: 1 };
console.log(a, b); // 1 2
let { a: b = 2 } = { a: 1 };
console.log(a); // 不存在 a 这个变量
console.log(b); // 1
对字符串的解构
length 属性,代表个数 let [a, b, c, d, e] = "hello"
console.log(a, b, c, d, e) // h e l l o
let { length } = "hello"
console.log(length) // 5
对数字和布尔值的解构
let { toString: s } = 123;
console.log(s === Number.prototype.toString) // true
let { toString: s } = true;
console.log(s === Boolean.prototype.toString) // true
对函数参数的解构
let arr = [[1,2], [3, 4]]
let res = arr.map([a, b] => a + b)
console.log(res) // [3, 7]
let arr = [1, undefined, 2]
let res = arr.map((a = 'test') => a);
console.log(res) // [1, 'test', 2]
let func = ({x, y} = {x: 0, y: 0}) => {
return [x, y]
}
console.log(func(1, 2)) // [undefined, undefined]
console.log(func()) // [0, 0]
console.log(func({})) // [undefined, undefined]
console.log(func({x: 1})) // [1, undefined]
let func = ({x=0, y=0}) => {
return [x, y]
}
console.log(func({x:1,y:2})) // [1, 2]
console.log(func()) // error
console.log(func({})) // [0, 0]
console.log(func({x: 1})) // [1, 0]
正则扩展
JS分格 和 perl 分格 let re = new RegExp('a'); //查找一个字符串内是否有a
let re = new RegExp('a', 'i'); //第一个是查找的对象,第二个是选项
let re = /a/; //查找一个字符串内是否有a
let re = /a/i;//第一个是查找的对象,第二个是选项
字符串扩展
大括号包含表示Unicode字符 //Unicode
console.log("a", "\u0061"); // a a
console.log("d", "\u{4E25}"); // d 严
let str = 'Domesy'
//codePointAt()
console.log(str.codePointAt(0)) // 68
//String.fromCharCode()
console.log(String.fromCharCode(68)) // D
//String.raw()
console.log(String.raw`Hi\n${1 + 2}`); // Hi\n3
console.log(`Hi\n${1 + 2}`); // Hi 3
let str = 'Domesy'
//startsWith()
console.log(str.startsWith("D")) // true
console.log(str.startsWith("s")) // false
//endsWith()
console.log(str.endsWith("y")) // true
console.log(str.endsWith("s")) // false
//repeat(): 所传的参数会自动向上取整,如果是字符串会转化为数字
console.log(str.repeat(2)) // DomesyDomesy
console.log(str.repeat(2.9)) // DomesyDomesy
// 遍历:for-of
for(let code of str){
console.log(code) // 一次返回 D o m e s y
}
//includes()
console.log(str.includes("s")) // true
console.log(str.includes("a")) // false
// trimStart()
const string = " Hello world! ";
console.log(string.trimStart()); // "Hello world! "
console.log(string.trimLeft()); // "Hello world! "
// trimEnd()
const string = " Hello world! ";
console.log(string.trimEnd()); // " Hello world!"
console.log(string.trimRight()); // " Hello world!"
其他
字符串模板 可单行可多行插入,使用 `
let str = `Dome
sy`
console.log(str) //会自动换行
// Dome
// sy
标签模板:
const str = {
name: '小杜杜',
info: '大家好‘
}
console.log(`${str.info}, 我是`${str.name}`) // 大家好,我是小杜杜
数组扩展
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
//Array.of()
let arr1 = Array.of(1, 2, 3);
console.log(arr1) // [1, 2, 3]
//copyWithin(): 三个参数 (target, start = 0, end = this.length)
// target: 目标的位置
// start: 开始位置,可以省略,可以是负数。
// end: 结束位置,可以省略,可以是负数,实际位置是end-1。
console.log(arr.copyWithin(0, 3, 5)) // [4, 5, 3, 4, 5]
//find()
console.log(arr.find((item) => item > 3 )) // 4
//findIndex()
console.log(arr.findIndex((item) => item > 3 )) // 3
// keys()
for (let index of arr.keys()) {
console.log(index); // 一次返回 0 1 2 3 4
}
// values()
for (let index of arr.values()) {
console.log(index); // 一次返回 1 2 3 4 5
}
// entries()
for (let index of arr.entries()) {
console.log(index); // 一次返回 [0, 1] [1, 2] [2, 3] [3, 4] [4, 5]
}
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// Array.from(): 遍历的可以是伪数组,如 String、Set结构,Node节点
let arr1 = Array.from([1, 3, 5], (item) => {
return item * 2;
})
console.log(arr1) // [2, 6, 10]
// fill(): 三个参数 (target, start = 0, end = this.length)
// target: 目标的位置
// start: 开始位置,可以省略,可以是负数。
// end: 结束位置,可以省略,可以是负数,实际位置是end-1。
console.log(arr.fill(7)) // [7, 7, 7, 7, 7]
console.log(arr.fill(7, 1, 3)) // [1, 7, 7, 4, 5]
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
//includes()
console.log(arr.includes(3)) // true
console.log([1, 2, NaN].includes(NaN)); // true
其他
扩展运算符:...
// 其作用为展开数组
let arr = [3, 4, 5]
console.log(...arr) // 3 4 5
let arr1 = [1, 2, ...arr]
console.log(...arr1) // 1 2 3 4 5
对象扩展
for-in//Object.is()
console.log(Object.is('abc', 'abc')) // true
console.log(Object.is([], [])) // false
//遍历:for-in
let obj = { name: 'Domesy', value: 'React' }
for(let key in obj){
console.log(key); // 依次返回属性值 name value
console.log(obj[key]); // 依次返回属性值 Domesy React
}
//Object.keys()
console.log(Object.keys(obj)) // ['name', 'value']
//Object.assign()
const target = { a: 1, b: 2 };
const source = { b: 4, c: 5 };
const result = Object.assign(target, source)
console.log(result) // {a: 1, b: 4, c: 5}
console.log(target) // {a: 1, b: 4, c: 5}
其他
简洁表示法
let a = 1;
let b = 2;
let obj = { a, b }
console.log(obj) // { a: 1, b: 2 }
let method = {
hello() {
console.log('hello')
}
}
console.log(method.hello())// hello
属性表达式: 直接用变量或者表达式来定义 Object 的 key
let a = "b"
let obj = {
[a]: "c"
}
console.log(obj) // {b : "c"}
扩展运算符 ...
// 其作用为展开数组
let { a, b, ...c } = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d: 4};
console.log(c) // {c: 3, d: 4}
let obj1 = { c: 3 }
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, ...obj1}
console.log(obj) // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}
数值扩展
0b 或 0B 开头,表示二进制00 或 0O 开头,表示二进制正数为1、负数为-1、正零 0、负零 -0、NaN
parseInt
parseFloat
//二进制
console.log(0b101) // 5
console.log(0o151) //105
//Number.isFinite()
console.log(Number.isFinite(7)); // true
console.log(Number.isFinite(true)); // false
//Number.isNaN()
console.log(Number.isNaN(NaN)); // true
console.log(Number.isNaN("true" / 0)); // true
console.log(Number.isNaN(true)); // false
//Number.isInteger()
console.log(Number.isInteger(17)); // true
console.log(Number.isInteger(17.58)); // false
//Number.isSafeInteger()
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(3)); // true
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(3.0)); // true
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger("3")); // false
console.log(Number.isSafeInteger(3.1)); // false
//Math.trunc()
console.log(Math.trunc(13.71)); // 13
console.log(Math.trunc(0)); // 0
console.log(Math.trunc(true)); // 1
console.log(Math.trunc(false)); // 0
//Math.sign()
console.log(Math.sign(3)); // 1
console.log(Math.sign(-3)); // -1
console.log(Math.sign(0)); // 0
console.log(Math.sign(-0)); // -0
console.log(Math.sign(NaN)); // NaN
console.log(Math.sign(true)); // 1
console.log(Math.sign(false)); // 0
//Math.abrt()
console.log(Math.cbrt(8)); // 2
//Number.parseInt()
console.log(Number.parseInt("6.71")); // 6
console.log(parseInt("6.71")); // 6
//Number.parseFloat()
console.log(Number.parseFloat("6.71@")); // 6.71
console.log(parseFloat("6.71@")); // 6.71
//参数默认赋值具体的数值
let x = 1
function fun(x, y = x){
console.log(x, y)
}
function fun1(c, y = x){
console.log(c, x, y)
}
fun(2); //2 2
fun1(1); //1 1 1
其他
Rest参数(扩展运算符 ...)
function fun(...arg){
console.log(arg) // [1, 2, 3, 4]
}
fun(1, 2, 3, 4)
箭头函数
let arrow = (v) => v + 2
console.log(arrow(1)) // 3
Set
const set = new Set()iterator对象,按插入顺序,为 [Key, Value] 形式 let list = new Set()
//add()
list.add("1")
list.add(1)
console(list) // Set(2) {1, "1"}
//size
console(list.size) // 2
//delete()
list.delete("1")
console(list) // Set(1) {1}
//has()
list.has(1) // true
list.has(3) // false
//clear()
list.clear()
console(list) // Set(0) {}
let arr = [{id: 1}, {id: 2}, {id: 3}]
let list = new Set(arr)
// keys()
for (let key of list.keys()) {
console.log(key); // 以此打印:{id: 1} {id: 2} {id: 3}
}
//values()
for (let key of list.values()) {
console.log(key); // 以此打印:{id: 1} {id: 2} {id: 3}
}
//entries()
for (let data of list.entries()) {
console.log(data); // 以此打印:[{id: 1},{id: 1}] [{id: 2},{id: 2}] [{id: 3},{id: 3}]
}
//forEach
list.forEach((item) => {
console.log(item)// 以此打印:{id: 1} {id: 2} {id: 3}
});
数组去重
new Set 无法去除对象 let arr = [1,1,'true','true',true,true,15,15,false,false, undefined,undefined, null,null, NaN, NaN,'NaN', 0, 0, 'a', 'a'];
console.log([...new Set(arr)])
//或
console.log(Array.from(new Set(arr)))
// [1, 'true', true, 15, false, undefined, null, NaN, 'NaN', 0, 'a']
可求并集,交集和差集
let a = new Set([1, 2, 3])
let b = new Set([2, 3, 4])
//并集
console.log(new Set([...a, ...b])) // Set(4) {1, 2, 3, 4}
//交集
console.log(new Set([...a].filter(v => b.has(v)))) // Set(2) {2, 3}
//差集
new Set([...a].filter(v => !b.has(v))) // Set(1) {1}
映射集合
let set = new Set([1,2,3])
console.log(new Set([...set].map(v => v * 2))) // Set(3) {2, 4, 6}
WeakSet
const set = new WeakSet()Map
const map = new Map() let map = new Map()
//set()
map.set('a', 1)
map.set('b', 2)
console.log(map) // Map(2) {'a' => 1, 'b' => 2}
//get
map.get("a") // 1
//size
console.log(map.size) // 2
//delete()
map.delete("a") // true
console.log(map) // Map(1) {'b' => 2}
//has()
map.has('b') // true
map.has(1) // false
//clear()
map.clear()
console.log(map) // Map(0) {}
let arr = [["a", 1], ["b", 2], ["c", 3]]
let map = new Map(arr)
// keys()
for (let key of map.keys()) {
console.log(key); // 以此打印:a b c
}
//values()
for (let value of map.values()) {
console.log(value); // 以此打印:1 2 3
}
//entries()
for (let data of map.entries()) {
console.log(data); // 以此打印:["a", 1] ["b", 2] ["c", 3]
}
//forEach
map.forEach((item) => {
console.log(item)// 以此打印:1 2 3
});
WeakMap
const set = new WeakMap()Symbol(原始类型)
独一无二的const sy = Stmbol()Symbol值,如存在此参数则返回原有的Symbol值(先搜索后创建,登记在全局环境)Symbol值的描述(只能返回Symbol.for()的key)Symbol值的数组 // 声明
let a = Symbol();
let b = Symbol();
console.log(a === b); // false
//Symbol.for()
let c = Symbol.for("domesy");
let d = Symbol.for("domesy");
console.log(c === d); // true
//Symbol.keyFor()
const e = Symbol.for("1");
console.log(Symbol.keyFor(e)); // 1
//Symbol.description
let symbol = Symbol("es");
console.log(symbol.description); // es
console.log(Symbol("es") === Symbol("es")); // false
console.log(symbol === symbol); // true
console.log(symbol.description === "es"); // true
Proxy
拦截,外界想要访问都要经过这层拦截,因此提供了一种机制,可以对外界的访问进行过滤和改写。代理器const proxy = new Proxy(target, handler) let obj = {
name: 'domesy',
time: '2022-01-27',
value: 1
}
let data = new Proxy(obj, {
//get()
get(target, key){
return target[key].replace("2022", '2015')
},
//set()
set(target, key, value) {
if (key === "name") {
return (target[key] = value);
} else {
return target[key];
}
},
// has()
has(target, key) {
if (key === "name") {
return target[key];
} else {
return false;
}
},
// deleteProperty()
deleteProperty(target, key) {
if (key.indexOf("_") > -1) {
delete target[key];
return true;
} else {
return target[key];
}
},
// ownKeys()
ownKeys(target) {
return Object.keys(target).filter((item) => item != "time");
},
})
console.log(data.time) // 2015-01-27
data.time = '2020'
data.name = 'React'
console.log(data) //Proxy {name: 'React', time: '2022-01-27', value: 1}
// 拦截has()
console.log("name" in data) // true
console.log("time" in data) // false
// 删除deleteProperty()
delete data.time; // true
// 遍历 ownKeys()
console.log(Object.keys(data)); //['name', 'value']
//apply()
let sum = (...args) => {
let num = 0;
args.forEach((item) => {
num += item;
});
return num;
};
sum = new Proxy(sum, {
apply(target, ctx, args) {
return target(...args) * 2;
},
});
console.log(sum(1, 2)); // 6
console.log(sum.call(null, 1, 2, 3)); // 12
console.log(sum.apply(null, [1, 2, 3])); // 12
//constructor()
let User = class {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
User = new Proxy(User, {
construct(target, args, newTarget) {
return new target(...args);
},
});
console.log(new User("domesy")); // User {name: 'domesy'}
Reflect
Object的默认行为Class
constructor() 基本定义和生成实例
class Parent {
constructor(name = 'es6'){
this.name = name
}
}
let data = new Parent('domesy')
console.log(data) // Parent { name: 'domesy'}
extends 继承
class Parent {
constructor(name = 'es6'){
this.name = name
}
}
// 普通继承
class Child extends Parent {}
console.log(new Child()) // Child { name: 'es6'}
// 传递参数
class Child extends Parent {
constructor(name = "child") {
super(name);
this.type = "child";
}
}
console.log(new Child('domesy')) // Child { name: 'domesy', type: 'child'}
getter setter
class Parent {
constructor(name = 'es6'){
this.name = name
}
// getter
get getName() {
return 'sy' + this.name
}
// setter
set setName(value){
this.name = value
}
}
let data = new Parent()
console.log(data.getName) // syes6
data.setName = 'domesy'
console.log(data.getName) // domesy
static 静态方法
class Parent {
static getName = (name) => {
return `你好!${name}`
}
}
console.log(Parent.getName('domesy')) // 你好!domesy
静态属性
class Parent {}
Parent.type = "test";
console.log(Parent.type); //test
Promise
Promise 就是为了解决“回调地狱”问题的,它可以将异步操作的处理变得很优雅。Promise 可以支持多个并发的请求,获取并发请求中的数据这个 Promise 可以解决异步的问题,本身不能说 Promise 是异步的基本用法
//普通定义
let ajax = (callback) => {
console.log('≈')
setTimeout(() => {
callback && callback.call();
}, 1000)
}
ajax(() => {
console.log('timeout')
})
// 先会打出 开始执行,1s 后打出 timeout
//Promise
let ajax = () => {
console.log("开始执行");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
};
ajax().then(() => {
console.log("timeout");
});
// 先会打出 开始执行,1s 后打出 timeout
// then()
let ajax = () => {
console.log("开始执行");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
};
ajax()
.then(() => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 2000);
});
})
.then(() => {
console.log("timeout")
})
// 先会打出 开始执行,3s(1+2) 后打出 timeout
// catch()
let ajax = (num) => {
console.log("开始执行");
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (num > 5) {
resolve();
} else {
throw new Error("出错了");
}
});
};
ajax(6)
.then(function () {
console.log("timeout"); // 先会打出 开始执行,1s 后打出 timeout
})
.catch(function (err) {
console.log("catch", err);
});
ajax(3)
.then(function () {
console.log("timeout");
})
.catch(function (err) {
console.log("catch"); // 先会打出 开始执行,1s 后打出 catch
});
Promise.all() 批量操作
//所有图片加载完成后添加到页面
const loadImg = (src) => {
return new Promise(resolve, reject) => {
let img = document.createElement("img");
img.src = src;
img.onload = function () {
resolve(img);
};
img.onerror = function (err) {
reject(err);
};
});
}
const showImgs = (imgs) => {
imgs.forEach((img) => {
document.body.appendChild(img);
})
}
Promise.all([
loadImg("https://ss0.baidu.com/7Po3dSag_xI4khGko9WTAnF6hhy/zhidao/pic/item/71cf3bc79f3df8dcc6551159cd11728b46102889.jpg"),
loadImg("https://ss0.baidu.com/7Po3dSag_xI4khGko9WTAnF6hhy/zhidao/pic/item/71cf3bc79f3df8dcc6551159cd11728b46102889.jpg"),
loadImg("https://ss0.baidu.com/7Po3dSag_xI4khGko9WTAnF6hhy/zhidao/pic/item/71cf3bc79f3df8dcc6551159cd11728b46102889.jpg"),
]).then(showImgs);
Promise.race()
//有一个执行完就回加载到页面
const loadImg = (src) => {
return new Promise(resolve, reject) => {
let img = document.createElement("img");
img.src = src;
img.onload = function () {
resolve(img);
};
img.onerror = function (err) {
reject(err);
};
});
}
const showImgs = (imgs) => {
let p = document.createElement("p");
p.appendChild(img);
document.body.appendChild(p);
}
Promise.race([
loadImg("https://ss0.baidu.com/7Po3dSag_xI4khGko9WTAnF6hhy/zhidao/pic/item/71cf3bc79f3df8dcc6551159cd11728b46102889.jpg"),
loadImg("https://ss0.baidu.com/7Po3dSag_xI4khGko9WTAnF6hhy/zhidao/pic/item/71cf3bc79f3df8dcc6551159cd11728b46102889.jpg"),
loadImg("https://ss0.baidu.com/7Po3dSag_xI4khGko9WTAnF6hhy/zhidao/pic/item/71cf3bc79f3df8dcc6551159cd11728b46102889.jpg"),
]).then(showImgs);
Promise的问题
Generator
value 和 done
value 代表值, done返回布尔(如果为false,代表后续还有,为true则已完成)恢复程序执行 let data = function* (){
yield "a";
yield "b";
return "c"
}
let generator = data();
console.log(generator.next()) //{value: 'a', done: false}
console.log(generator.next()) //{value: 'b', done: false}
console.log(generator.next()) //{value: 'c', done: true}
console.log(generator.next()) //{value: undefined, done: true}
Iterator 遍历器
数组、某些类似数组的对象、Set和Map结构。 // 基本使用
let arr = ["hello", "world"];
let map = arr[Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(map.next()); // {value: 'hello', done: false}
console.log(map.next()); // {value: 'world', done: false}
console.log(map.next()); // {value: undefined, done: true}
// for of 循环
let arr = ["hello", "world"];
for (let value of arr) {
console.log(value); // hello world
}
// 对象处理
let obj = {
start: [1, 5, 2],
end: [7, 9, 6],
[Symbol.iterator](){
let index = 0;
let arr = this.start.concat(this.end)
return {
next(){
if(index < arr.length){
return {
value: arr[index++],
done: false
}
}else{
return {
value: arr[index++],
done: true
}
}
}
}
}
}
for (let key of obj) {
console.log(key); // 1 5 2 7 9 6
}
Decorator 装饰器
@符号,用来扩展,修改类的行为core-decorators
const name = (target) => {
target.name = "domesy"
}
@name
class Test{}
console.log(Test.name) //domesy
模块化
export 导出模块
export default Index
export { name as newName }
import 导入模块
import Index from './Index'
import * as Index from './Index'
import { name, value, id } from './Index'
import { name as newName } from './Index'
import './Index'
import Index, { name, value, id } from './Index'
复合模式
export命令和import命令结合在一起写成一行,变量实质没有被导入当前模块,相当于对外转发接口,导致当前模块无法直接使用其导入变量,适用于 全部子模块导出数组扩展
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
//includes() ES6
console.log(arr.includes(3)) // true
console.log([1, 2, NaN].includes(NaN)); // true
// includes() ES7
console.log(arr.includes(1, 0)) // true
console.log(arr.includes(1, 1)) // false
数值扩展
** 代表 Math.pow()
// 幂运算符 ES7
console.log(Math.pow(2, 3)) // 8
console.log(2 ** 8) // 256
字符传扩展
let str = 'Domesy'
//padStart(): 会以空格的形式补位吗,这里用0代替,第二个参数会定义一个模板形式,会以模板进行替换
console.log("1".padStart(2, "0")); // 01
console.log("8-27".padStart(10, "YYYY-0M-0D")); // YYYY-08-27
// padEnd():与padStart()用法相同
console.log("1".padEnd(2, "0")); // 10
对象扩展
let obj = { name: 'Domesy', value: 'React' }
//Object.values()
console.log(Object.values(obj)) // ['React', 'React']
//Object.entries()
console.log(Object.entries(obj)) // [['name', 'value'], ['React', 'React']]
async await
const func = async () => {
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("执行");
}, 1000);
});
console.log(await promise);
console.log(await 0);
console.log(await Promise.resolve(1));
console.log(2);
return Promise.resolve(3);
}
func().then(val => {
console.log(val); // 依次执行: 执行 0 1 2 3
});
Promise对象,因此可以使用 then
forEach() 执行 async/await会失效,可以使用 for-of 和 Promise.all()代替reject 对象,需要使用 try catch 来捕捉awiait 等到了之后做了什么?
async await 与 promise 的优缺点
字符传扩展
undefined,并且从raw上可获取原字符串。 // 放松字符串的限制
const test = (value) => {
console.log(value)
}
test `domesy` // ['domesy', raw: ["domesy"]]
Promise
let func = time => {
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if(time < 500){
res(time)
}else{
rej(time)
}
}, time)
})
}
func(300)
.then((val) => console.log('res', val))
.catch((erro) => console.log('rej', erro))
.finally(() => console.log('完成'))
// 执行结果: res 300 完成
func(700)
.then((val) => console.log('res', val))
.catch((erro) => console.log('rej', erro))
.finally(() => console.log('完成'))
// 执行结果: rej 700 完成
for-await-of
Promise对象变为resolved状态才进入下一步 let getTime = (seconds) => {
return new Promise(res => {
setTimeout(() => {
res(seconds)
}, seconds)
})
}
async function test(){
let arr = [getTime(2000),getTime(500),getTime(1000)]
for await (let x of arr){
console.log(x);
}
}
test() //以此执行 2000 500 1000
字符传扩展
//JSON.stringify() 升级
console.log(JSON.stringify("\uD83D\uDE0E"));
console.log(JSON.stringify("\u{D800}")); // \ud800
数组扩展
Infinity 自动解到最底层)) let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
// flatMap()
console.log(arr.map((x) => [x * 2])); // [ [ 2 ], [ 4 ], [ 6 ], [ 8 ] ]
console.log(arr.flatMap((x) => [x * 2])); // [ 2, 4, 6, 8 ]
console.log(arr.flatMap((x) => [[x * 2]])); // [ [ 2 ], [ 4 ], [ 6 ], [ 8 ] ]
const arr1 = [0, 1, 2, [3, 4]];
const arr2 = [0, 1, 2, [[[3, 4]]]];
console.log(arr1.flat()); // [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
console.log(arr2.flat(2)); // [ 0, 1, 2, [ 3, 4 ] ]
console.log(arr2.flat(Infinity)); // [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
对象扩展
Object.fromEntries()
Object.entries()的逆操作Map 转化为 Object
let map = new Map([
["a", 1],
["b", 2],
]);
let obj = Object.fromEntries(map);
console.log(obj); // {a: 1, b: 2}
Array 转化为 Object
// 注意数组的形式
let arr = [
["a", 1],
["b", 2],
]
let obj = Object.fromEntries(arr);
console.log(obj); // {a: 1, b: 2}
对象转换
let obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3
}
let res = Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(obj).filter(([key, val]) => value !== 3)
)
console.log(res) //{a: 1, b: 2}
数值扩展
//toString()
function test () {
consople.log('domesy')
}
console.log(test.toString());
// function test () {
// consople.log('domesy')
// }
可选的Catch参数
let func = (name) => {
try {
return JSON.parse(name)
} catch {
return false
}
}
console.log(func(1)) // 1
console.log(func({a: '1'})) // false
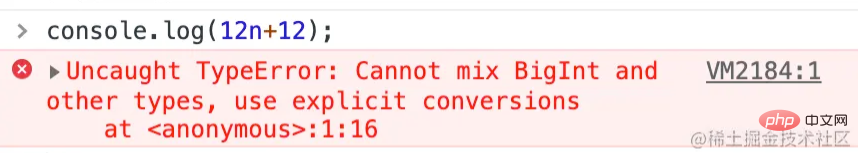
BigInt(原始类型)
// Number
console.log(2 ** 53) // 9007199254740992
console.log(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) // 9007199254740991
//BigInt
const bigInt = 9007199254740993n
console.log(bigInt) // 9007199254740993n
console.log(typeof bigInt) // bigint
console.log(1n == 1) // true
console.log(1n === 1) // false
const bigIntNum = BigInt(9007199254740993n)
console.log(bigIntNum) // 9007199254740993n
基本数据类型
srting、number、boolean、object、null、undefined、symbolobject 包含: Array、Function、Date、RegExpsrting、number、boolean、object、null、undefined、symbol、BigIntPromise
Promise.all()
Promise.allSettled([
Promise.reject({
code: 500,
msg: "服务异常",
}),
Promise.resolve({
code: 200,
data: ["1", "2", "3"],
}),
Promise.resolve({
code: 200,
data: ["4", "5", "6"],
}),
]).then((res) =>{
console.log(res) // [{ reason: {code: 500, msg: '服务异常'}, status: "rejected" },
// { reason: {code: 200, data: ["1", "2", "3"]}, status: "rejected" },
// { reason: {code: 200, data: ["4", "5", "6"]}, status: "rejected" }]
const data = res.filter((item) => item.status === "fulfilled");
console.log(data); // [{ reason: {code: 200, data: ["1", "2", "3"]}, status: "rejected" },
// { reason: {code: 200, data: ["4", "5", "6"]}, status: "rejected" }]
})
import(): 动态导入
require的区别是:require()是同步加载,import()是异步加载
// then()
let modulePage = "index.js";
import(modulePage).then((module) => {
module.init();
});
// 结合 async await
(async () => {
const modulePage = 'index.js'
const module = await import(modulePage);
console.log(module)
})
globalThis
// 浏览器环境
console.log(globalThis) // window
// node
console.log(globalThis) // global
可选链
const user = { name: 'domesy' }
//ES11之前
let a = user && user.name
//现在
let b = user?.name
空值合并运算符
"" || "default value"; // default value
"" ?? "default value"; // ""
const b = 0;
const a = b || 5;
console.log(a); // 5
const b = null // undefined
const a = b ?? 123;
console.log(a); // 123
字符传扩展
let str = "Hi!,这是ES6~ES12的新特性,目前为ES12"
console.log(str.replace("ES", "SY")); // Hi!,这是SY6~ES12的新特性,目前为ES12
console.log(str.replace(/ES/g, "Sy")); // Hi!,这是Sy6~Sy12的新特性,目前为Sy12
console.log(str.replaceAll("ES", "Sy")); // Hi!,这是Sy6~Sy12的新特性,目前为Sy12
console.log(str.replaceAll(/ES/g, "Sy")); // Hi!,这是Sy6~Sy12的新特性,目前为Sy12
Promise
Promise.any([
Promise.reject("Third"),
Promise.resolve("Second"),
Promise.resolve("First"),
])
.then((res) => console.log(res)) // Second
.catch((err) => console.error(err));
Promise.any([
Promise.reject("Error 1"),
Promise.reject("Error 2"),
Promise.reject("Error 3"),
])
.then((res) => console.log(res))
.catch((err) => console.error(err));
// AggregateError: All promises were rejected
Promise.any([
Promise.resolve("Third"),
Promise.resolve("Second"),
Promise.resolve("First"),
])
.then((res) => console.log(res)) // Third
.catch((err) => console.error(err));
WeakRefs
let weakref = new WeakRef({name: 'domesy', year: 24})
weakref.deref() // {name: 'domesy', year: 24}
weakref.deref().year // 24
逻辑操作符和赋值表达
&&=
let num1 = 5;
let num2 = 10;
num1 &&= num2;
console.log(num1); // 10
// 等价于
num1 && (num1 = num2);
if (num1) {
num1 = num2;
}
||=
let num1;
let num2 = 10;
num1 ||= num2;
console.log(num1); // 10
// 等价于
num1 || (num1 = num2);
if (!num1) {
num1 = num2;
}
??=
let num1;
let num2 = 10;
let num3 = null; // undefined
num1 ??= num2;
console.log(num1); // 10
num1 = false;
num1 ??= num2;
console.log(num1); // false
num3 ??= 123;
console.log(num3); // 123
// 等价于
// num1 ?? (num1 = num2);
数值分隔符
let num1 = 100000;
let num2 = 100_000;
console.log(num1); // 100000
console.log(num2); // 100000
const num3 = 10.12_34_56
console.log(num3); // 10.123456

声明:本文转载于:掘金社区,如有侵犯,请联系admin@php.cn删除
程序员必备接口测试调试工具:点击使用
声明:本文转载于网络,如有侵犯,请联系545125923@qq.com删除
